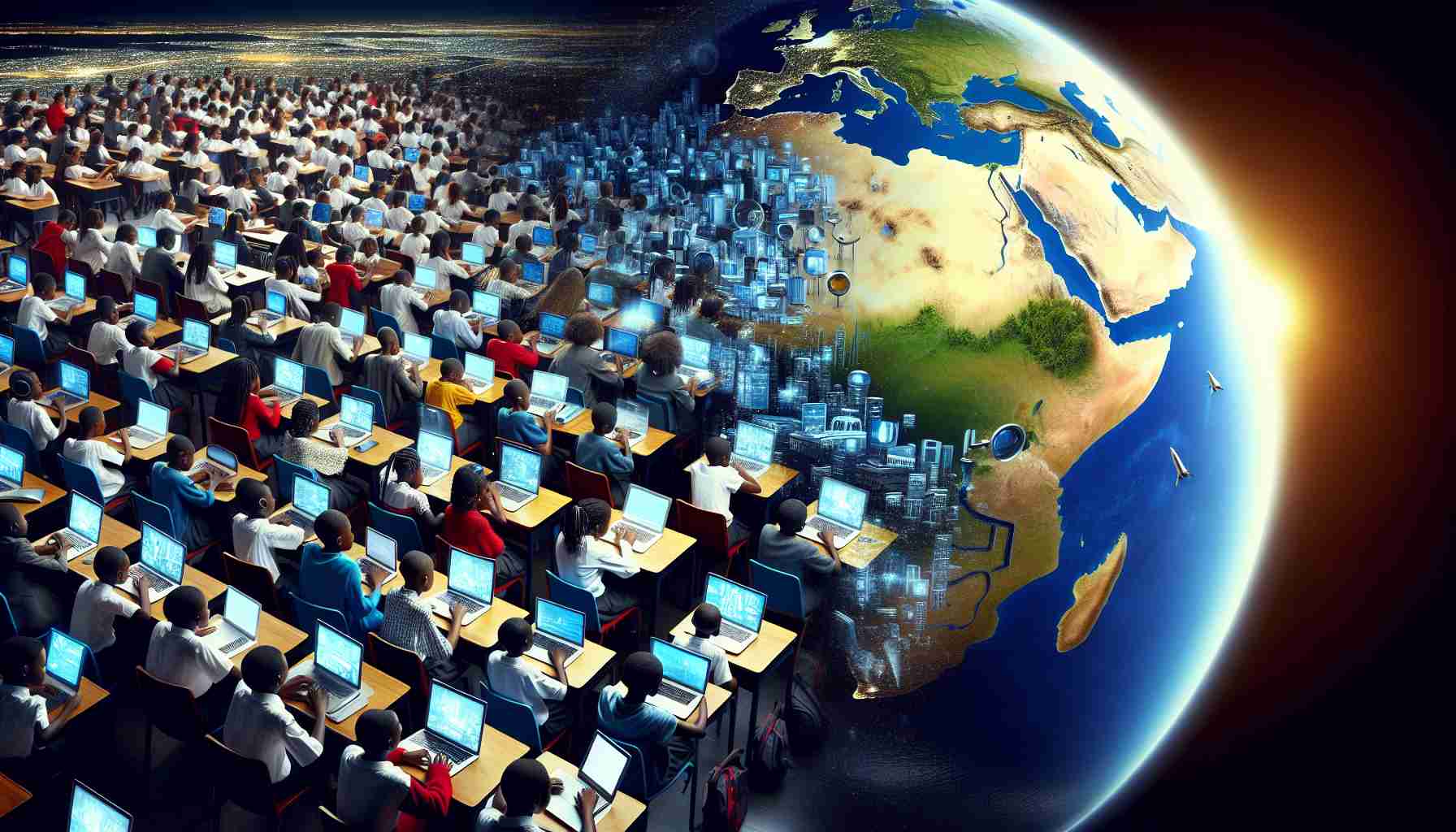
- Africa is experiencing a digital learning transformation post-pandemic, significantly impacting education across the continent.
- The African e-learning market is projected to grow from $3.4 billion in 2024 to $7.7 billion by 2033.
- Digital education is essential due to limited physical educational infrastructure and a growing young population.
- The pandemic accelerated the adoption of virtual learning, pushing educators and learners to adapt to online platforms.
- Technology bridges educational gaps, providing vast resources and opportunities for students regardless of location.
- Partnerships between governments, NGOs, and tech companies are driving the development of locally relevant content.
- Africa’s e-learning movement represents a broader commitment to making education accessible and equitable through technology.
As the dust settles after the global upheaval of the pandemic, a quiet revolution is taking hold across Africa—a digital learning renaissance that is transforming education from bustling Nigerian classrooms to remote Kenyan villages. With vibrant enthusiasm, the African e-learning market is poised to soar from a modest $3.4 billion in 2024 to an awe-inspiring $7.7 billion by 2033.
This surge isn’t simply about numbers; it’s about the continent’s youthful pulse demanding knowledge. A burgeoning young population is facing a scarcity of physical educational infrastructure. In this landscape, digital learning isn’t just a choice—it’s a necessity. Doors to new opportunities swing open for students, ushering in a future where geography no longer chains talent to fate.
The pandemic served as an unexpected catalyst, igniting a shift that now sees both educators and learners embracing virtual platforms. Schools and universities pivoted to online courses, quickly adapting curricula to ensure no mind was left behind. Technology not only bridges gaps but also expands horizons, offering a veritable library of resources right at one’s fingertips.
The engine driving this leap is a blend of innovation and investment. Governments and NGOs are forging partnerships with tech giants, blending local flavor with global tech prowess. These collaborations have sparked the growth of tailored content—digital textbooks and interactive modules that speak the languages and stories of local communities.
The key takeaway? Africa’s e-learning momentum signals more than growth in market value. It reflects a transformation, a commitment to harnessing technology for empowerment. As educators and innovators continue to ride this digital wave, they craft a narrative where knowledge is accessible, equitable, and vibrant—a narrative of hope and progress for an entire continent.
A Digital Learning Renaissance: Unlocking Africa’s Educational Future
### The E-Learning Boom in Africa: Opportunities and Challenges
Africa’s educational landscape is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by the surge in digital learning. Following the pandemic, there’s been a notable shift towards e-learning platforms, providing hope for addressing educational disparities across the continent. Yet, beyond this optimistic narrative, there are crucial aspects that warrant further exploration:
#### How-To: Implementing E-Learning Solutions in Africa
Implementing effective e-learning solutions requires a nuanced approach. Key steps include:
1. **Infrastructure Development**: Strengthening internet connectivity and providing affordable access to digital devices are critical.
2. **Curriculum Adaptation**: Localizing content to resonate with African cultures and languages ensures relevance and engagement.
3. **Capacity Building**: Training educators in digital tools enhances the teaching experience and equips them to deliver quality education remotely.
#### Pros and Cons of E-Learning Adoption
**Pros**:
– **Accessibility**: Breaks down geographic barriers, offering education to remote or underserved regions.
– **Flexibility**: Students learn at their own pace and have access to a broader range of resources.
– **Scalability**: Easier to scale compared to traditional education models.
**Cons**:
– **Digital Divide**: Limited access to technology in rural areas could widen educational gaps.
– **Quality Control**: Ensuring the content’s quality and relevance can be challenging without proper oversight.
– **Student Engagement**: Maintaining student engagement remotely can be difficult.
#### Market Forecasts and Trends
The African e-learning market is projected to grow from $3.4 billion in 2024 to $7.7 billion by 2033. Key trends include:
– **Mobile Learning**: The proliferation of smartphones is driving mobile-optimized educational content.
– **AI and VR**: Integration of AI for personalized learning experiences and VR for virtual classrooms is on the rise.
– **Collaboration Platforms**: Growing partnerships between local governments, NGOs, and tech companies to create tailored educational solutions.
#### Reviews and Innovations
Recent reviews highlight the success stories emerging from those who have embraced e-learning, with innovative practices such as gamification and the use of local storytelling in digital tools proving effective in engaging students.
#### Security Aspects and Sustainability
Ensuring data security on digital platforms is paramount. Programs should focus on:
– **Data Protection**: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures to protect student information.
– **Sustainable Practices**: Utilizing renewable energy sources for powering digital infrastructures and focusing on e-waste management.
#### Key Questions and Answers
– **How is e-learning impacting rural education in Africa?**
– It’s expanding access to quality education and resources, previously limited or unavailable in these areas.
– **What role are tech giants playing in this transformation?**
– Companies like Google and Microsoft are partnering with local organizations to provide infrastructure support, learning platforms, and skill training.
– **How can e-learning be made more inclusive?**
– By developing more localized content, improving technology access, and creating diverse learning modules that cater to varying educational needs.
For more information on technology’s transformative role in education, visit UNESCO and edX.