Call to Action for Electric Vehicle Infrastructure
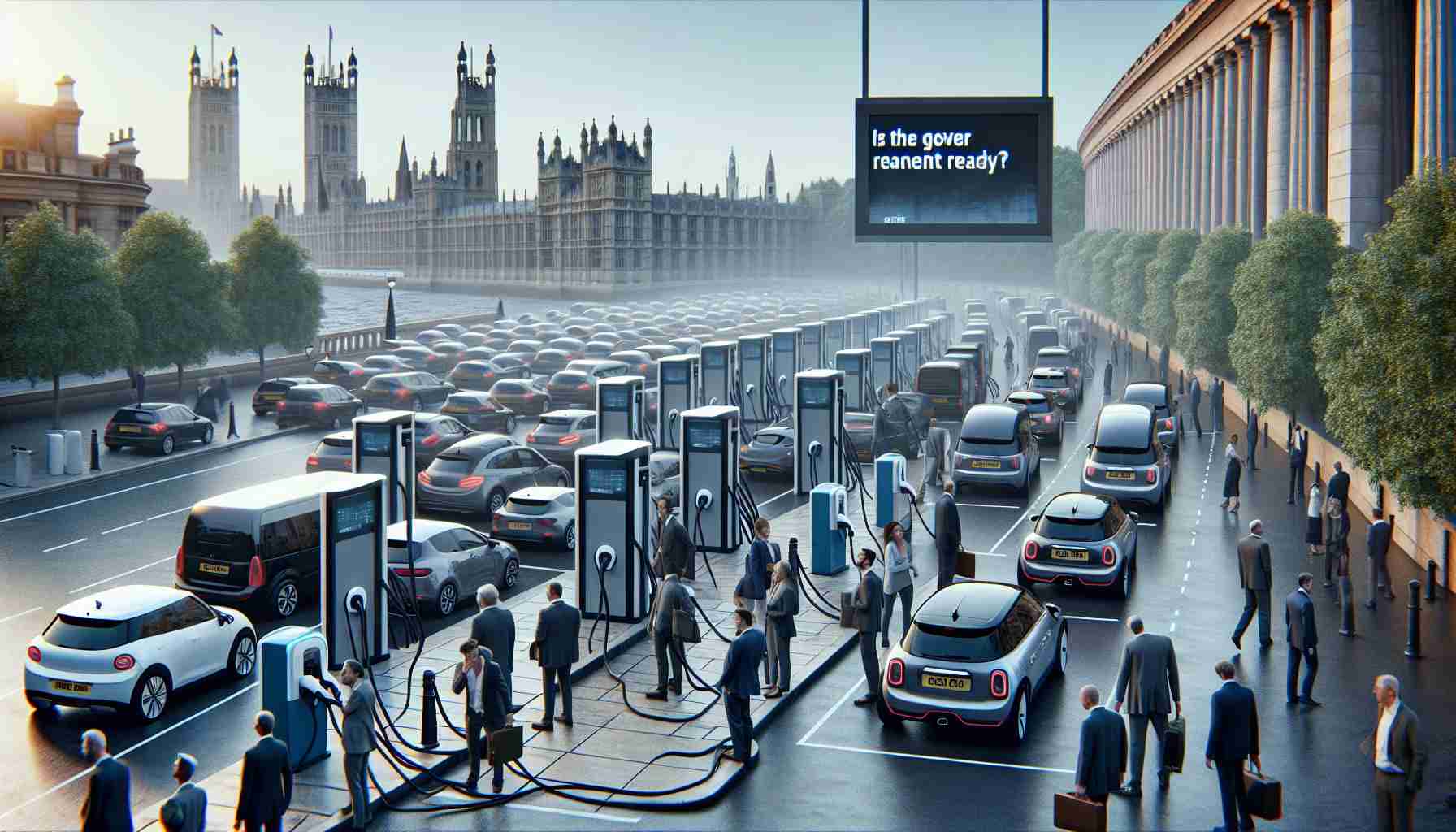
A warning message sent to the UK government emphasizes the urgent need to overhaul the electric vehicle (EV) charging strategy. The Labour Party has highlighted the necessity for a revised funding approach as the nation prepares to fully transition from petrol and diesel vehicles by 2030.
Experts advocate for strategies that attract private investment and build robust long-term charging solutions. As the popularity of electric vehicles rises and larger batteries emerge, reliance on low-power charging stations is becoming unrealistic. The focus now needs to shift towards high-speed chargers that can accommodate the evolving demand for electric vehicles.
To better prepare for the future of transportation, it is proposed as a quick solution to allocate funding to necessary areas, encourage local authorities to utilize available land for private investment, and prioritize the installation of high-speed chargers. These measures will significantly contribute to the UK achieving widespread electric vehicle adoption.
Concerns have been raised about the current distribution of charging points. While those who can charge at home and certain destination charging hubs have sufficient stations, many potential EV users lack adequate options. The National Audit Office predicts that the government will meet its target of 300,000 public chargers by 2030, but skepticism remains regarding the feasibility of these projections, highlighting the need for a more comprehensive approach to infrastructure development.
Wider Implications of Overhauling Electric Vehicle Infrastructure
The urgent call for a strong electric vehicle (EV) charging strategy has wide-ranging implications for society, culture, and the global economy. As the UK pushes for a full transition to EVs by 2030, this infrastructure reform could serve as a catalyst for a cultural shift towards sustainability. Increased accessibility to EV charging stations will democratize electric vehicle usage, prompting urban planners and developers to rethink space utilization, transforming public areas to accommodate this essential infrastructure.
From an economic perspective, a concentrated focus on EV infrastructure could stimulate private sector investment. The global EV market is expected to reach nearly $1 trillion by 2025, driving job creation and innovation in clean technologies. Additionally, a well-developed charging network can enhance consumer confidence in EVs, increasing adoption rates and ultimately supporting local economies through increased electric vehicle sales and services.
Environmentally, improved charging infrastructure is likely to accelerate the transition away from fossil fuels, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions. However, this transition must balance sustainable practices in material sourcing and lifecycle management for EV batteries and components, minimizing ecological footprints as we enter a new era of transportation.
Looking ahead, embracing a robust EV infrastructure will not only strengthen the UK’s leadership in sustainability but also set a precedent for other countries to follow, shaping a global trend towards clean transportation and a more sustainable future.
Overhauling EV Infrastructure for a Sustainable Future: Call to Action
Introduction
As the UK accelerates towards a fully electric vehicle (EV) future by 2030, the urgency to strengthen EV charging infrastructure has never been greater. Recent discussions led by the Labour Party emphasize the need for a strategic overhaul of the existing charging framework to accommodate new technologies and investment pathways. This article explores key aspects of the EV infrastructure transformation, innovations, limitations, and future prospects.
Current Issues with EV Charging Infrastructure
1. Distribution Imbalance: Urban areas benefit from sufficient charging stations, while rural regions often lack accessible options. This imbalance complicates the transition for potential EV owners, especially those without home charging solutions.
2. Charging Speed and Technology: Reliance on low-power charging stations is becoming increasingly inadequate. EVs are being equipped with larger batteries that require high-speed chargers to minimize downtime and enhance user experience.
3. Reality vs. Government Goals: The National Audit Office predicts that the UK will achieve its target of 300,000 public chargers by 2030. However, skepticism exists regarding the feasibility of these projections, suggesting that a more proactive approach to infrastructure development is necessary.
Recommendations for Future Infrastructure
– Inviting Private Investment: To diversify funding sources and encourage innovation, the government should invite private companies to invest in high-capacity charging solutions. This approach can enable faster deployment and modernization of the charging network.
– Utilizing Local Land: Local authorities should leverage available land for the installation of charging stations to improve accessibility, which could include collaborating with businesses to create charging hubs.
– Focusing on High-Speed Chargers: Transitioning to high-performance chargers will help maintain infrastructure aligned with the increasing battery capacities of new electric vehicles. Targeted funding support for these installations can significantly enhance consumer adoption.
Pros and Cons of Current EV Charging Strategy
Pros:
– Growing awareness and popularity of EVs among the public.
– Government incentives for EV purchases can boost usage rates.
– Potential for job creation in the EV charging sector.
Cons:
– Infrastructure deficiencies in rural areas may pose barriers for potential users.
– High costs associated with installing advanced charging stations.
– Ongoing issues with the reliability and efficiency of the power grid.
Future Trends in EV Charging Technology
1. Wireless Charging: Research into inductive charging technology promises a future where EVs can charge simply by parking over a special pad, eliminating the need for cables.
2. Smart Charging Solutions: These systems enable demand-based dynamic pricing, optimizing the best charging times and costs for users while reducing the burden on the power grid during peak hours.
3. Integration of Energy Storage: The integration of charging stations with renewable energy sources and energy storage can enhance reliability and sustainability. Solar-powered charging stations are a growing trend that reduces dependence on grid electricity.
Conclusion
As the UK moves towards its 2030 EV adoption target, the urgency to overhaul EV charging infrastructure becomes increasingly clear. By embracing innovative technologies, attracting private investment, and strategically targeting the most needed areas, the government can build a strong and inclusive charging network. This proactive approach will not only facilitate the transition to electric vehicles but also contribute to a sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation future.
For more information on electric vehicle initiatives and infrastructure development, visit the UK Government.